Natural Gas is the cleanest fossil fuel for Cogeneration systems. Different Cogeneration system configurations have been devised to work with different types of fossil fuels, ranging from natural gas & fuel oil to coal. Nevertheless, Natural Gas is undisputably the cleanest fuel option available in terms of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) emissions.
Contents
What determines the Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions of Fuel?
The quantity of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) produced by a fuel is dependent on the amount of carbon in the fuel, and the heat value of a fuel is determined by its hydrocarbon composition. Amongst the complex hydrocarbon molecules, Methane (CH4), with its simple molecular structure, has the highest heat produced per unit mass, i.e. 55.7kJ/g. Due to the high percentage of Methane (CH4) in its composition (typically ranging from 70% to 90%), Natural Gas has the lowest Carbon Dioxide (CO2) emission rate relative to the energy generated during combustion.
The table below summarizes the Carbon Dioxide (CO2) emissions (CDE) (quantity of CO2) per unit of energy generated during combustion, for different types of fossil fuels. Natural Gas is indisputably the cleanest fossil fuel for Cogeneration systems, with Carbon Dioxide (CO2) emissions being 27.4% and 43.1% lower than Diesel and Bituminous Coal respectively.

How to estimate Carbon Dioxide (CO2) emissions for power generation?
The formula for estimating the carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions for a particular power generation plant or technology is as follows:

Carbon Dioxide (CO2) emissions for different fossil fuel power plants
From the above formula, the Carbon Dioxide (CO2) emissions from different fossil fuel power plants can be estimated as follows:
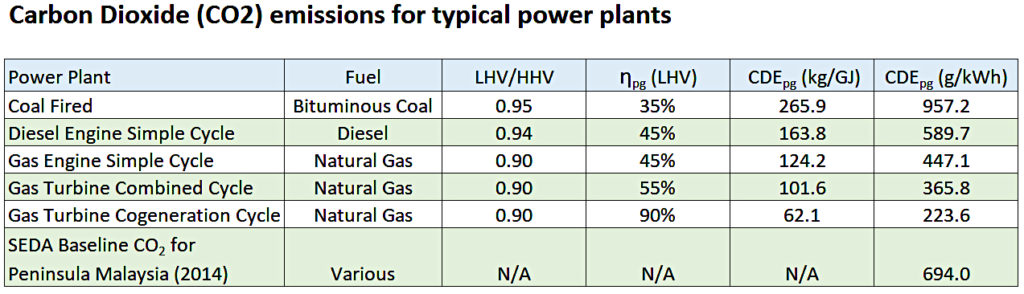
(SEDA Baseline CO2 for Peninsula Malaysia)
How to improve energy efficiency and reduce Carbon Dioxide (CO2) emissions of the power generation sector?
As shown in the paragraph above, power generation technology using Natural Gas have the lowest Carbon Dioxide (CO2) emissions per unit of generated energy, in addition to having higher primary fuel efficiency compared to coal fired power plants. Hence increasing the use of Natural Gas in the fuel mix of the power generation sector will lower the Carbon Dioxide (CO2) emissions while increasing the generation efficiency.
Despite the substantial growth in the adoption of renewable energy technology, fossil fuels still play a major role in the power generation mix of many countries. For example, in Malaysia fossil fuels command more than 80% share of the generation mix (as stated in the Malaysia Energy Statistics Handbook 2018). These countries would do well to increase the use of Natural Gas and to adopt more Cogeneration systems in order to improve the primary energy efficiency as well as to reduce the Carbon emissions of the power generation sector.
